“Shipwreck” and “North Dakota” are not words one might normally expect to hear in the same sentence. However, there is a well-documented historical use of the region’s waterways.
The first use of steamboats for trade and passenger transportation in the territory that would become the state of North Dakota occurred during the fur trade era of 1830-1867. At that time, steamboat traffic on the Upper Missouri was a common sight, as furs were moved to downriver markets in St. Louis and beyond. The use of steamboats by the military during the Plains Indian Wars (1860-1890) is also well documented, especially during the various punitive campaigns of the period. Later steamboat traffic in the Dakotas centered around providing transportation and facilitating commerce in the region. As the railroads expanded, steamboats increasingly found it more difficult to remain profitable as they were routinely outcompeted for the transport of both passengers and freight.
The story of the steamboat Abner O’Neal begins in these waning days of commercially viable steamboat traffic on the Upper Missouri.

Postcard of a colorized photograph of the steamboat Abner O’Neal (1884-1892). SHSND SA B0735-00001
The Abner O'Neal steamboat was built in 1884 in Freedom, Pennsylvania, for the Steubenville, Ohio/Wheeling, West Virginia-area steamboat trade. Her original namesake Capt. Abner O'Neal and his son, the boat owner Capt. George O'Neal, were well-known figures during the 1870s in the Steubenville/Wheeling steamboat industry. The Abner O’Neal operated successfully in that region for several years transporting freight and passengers. She was then sold to the Missouri River Transportation Company in March 1890, and Capt. Sam V. Williamson moved to extend his pilot’s license to operate on the Missouri River in North Dakota and South Dakota.
By November 1890, the Abner O’Neal had been operating in the passenger and freight trade on the Missouri for a few months. According to the Pierre Weekly Free Press, citizens in the town turned out “to see a real live steamboat” and marvel at “the practical demonstration of the navigability of the Missouri River” when the Abner O’Neal docked there. Soon the reality of the seasonal “navigability of the Missouri River” would become painfully clear, however.

A Pierre Weekly Free Press (S.D.) report from Nov. 11, 1890, reflected the interest the steamboat generated among locals.
We know the Abner O’Neal spent much of her time in this region transporting grain (usually wheat) between the cities of Washburn and Bismarck/Mandan. The nearby Painted Woods area of the Missouri River has long been recognized as a difficult spot for navigation. (It still is.) The area is known for treacherous sand bars and frequent tree snags that can rip a boat hull wide open. By late November 1891, the Abner O’Neal had become stuck in early-winter ice in the Painted Woods area with a cargo of grain on board.

The November 20, 1891, edition of the Bismarck Weekly Tribune noted that the Abner O’Neal had become stuck in the ice in a treacherous part of the Missouri River.
The Abner O’Neal remained stuck there in the ice for another four months, until she was finally freed in early April 1892. We have further documentation that the crew of the steamboat labored to keep the hull free from the ice by chopping the ice in direct contact with the hull. Steamboats operating in the Bismarck/Mandan area were routinely hauled out of the river during the winter months to avoid this very situation. We could speculate what lasting effect wintering in the Painted Woods area may have had on the integrity of the Abner O’Neal’s hull, but by late April 1892, the boat was once again making trips transporting grain from Washburn to the Bismarck/Mandan roller mills for processing.

On April 9, 1892, The Washburn Leader (N.D.) recounted the steamboat’s joyful reception.
On the afternoon of July 17, 1892, the Abner O’Neal was transporting 9,000 bushels of wheat from Washburn to the Mandan roller mill when it struck a submerged snag or rock and began to sink. The crew attempted to patch the hole, but the damage was too extensive and the steamboat quickly went down in 8-to-10 feet of water. The boat and cargo were uninsured and considered a total loss.

The July 22, 1892, Bismarck Weekly Tribune carried this description of the sinking of the Abner O'Neal.
For nearly 130 years, the steamboat survived seasonal exposures as a result of fall drawdowns at Lake Sakakawea and the subsequent winter freezes. In late September 2020, State Historical Society of North Dakota archaeologists received notification from the boating public that the Abner O’Neal wreck location was visible due to current low water conditions. Consent to access the wreck site was granted by an adjacent landowner, and images and video of the wreck location were obtained via unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) carrying visible light cameras and a 10-band multispectral sensor on Oct. 1-2, 2020. Researchers generated high-resolution orthophoto mosaics from the images collected by the visible light camera and multispectral sensor. A detailed analysis of the orthophoto mosaics, video, and multispectral images collected by agency archaeologists is ongoing.
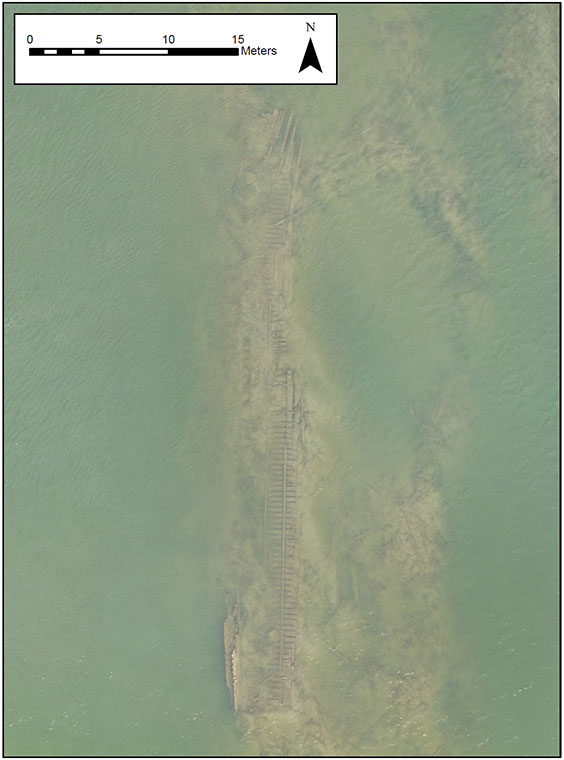

A high-resolution orthophoto mosaic of the Abner O’Neal wreck produced from images captured by the agency’s drone on Oct. 2, 2020.
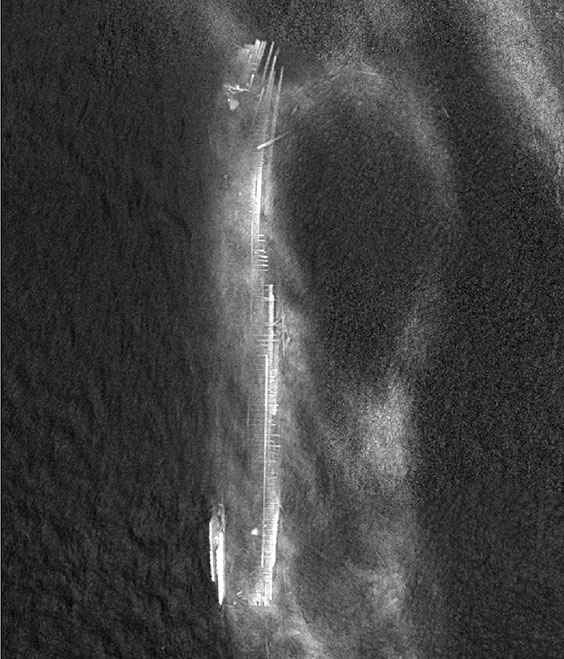
Near-infrared image of the Abner O’Neal wreck captured by the agency drone on Oct. 2, 2020.
The wreck of the Abner O’Neal was salvaged after the sinking, with the superstructure and paddle wheel removed. Much of the hull of the wreck has remained intact, despite being submerged in the Missouri River for 128 years. The wreck has been periodically subjected to non-systematic collecting by the public since the sinking. The State Historical Society has received a few artifacts donated by private collectors since 1958, but no artifacts were collected by our archaeologists during our October 2020 site investigations.
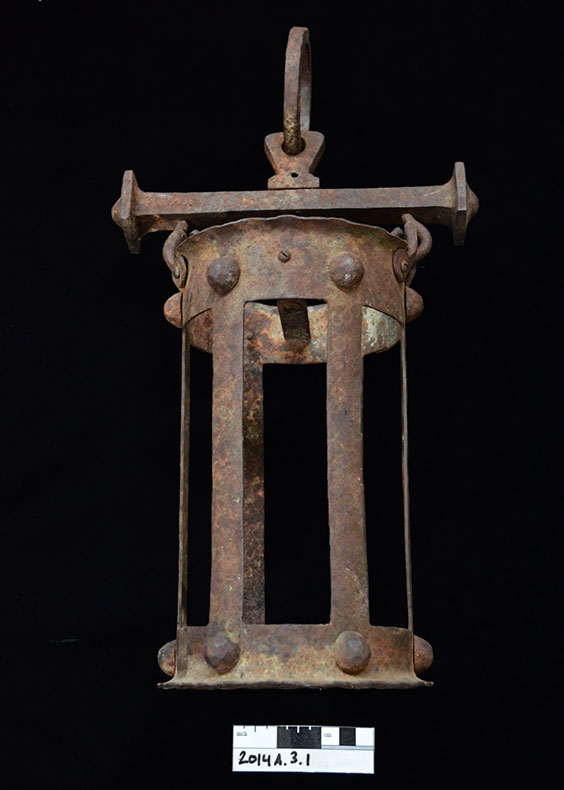

A lantern from the Abner O’Neal was donated to the State Historical Society by a private collector. SHSND 2014.A.3.1.
The Abner O’Neal is within the boundaries of state-sovereign lands managed by North Dakota. Several federal and state regulations protect the site and prohibit the collection of artifacts from the location. Boaters and other interested parties are encouraged to avoid the wreck as a navigational obstacle and reminded to take only pictures.

The sun sets on the wreck of the Abner O’Neal, September 2020. Image courtesy of Jesse Biesterfeld.
*This blog was co-authored with Andrew Clark.

