“Where did you find it?” This is, without question, the first thing you will hear any of our archaeologists ask when someone shows us an artifact. We are kind of obsessed with the “where” questions – where did you find it? Where did it come from? Where in the excavation unit was it found? What vertical level did it come from? Where was it in relation to (fill in the blank)? Where in the world did I put my trowel? (You wouldn’t believe how often I’ve asked the last one.) The “where” – technically known as provenience or context – is crucial to the artifact’s ability to tell a story. If you are a regular reader, then you already know that the object itself can provide some information about the human past. But if we don’t know its context, then it is pretty limited in terms of scientific value.
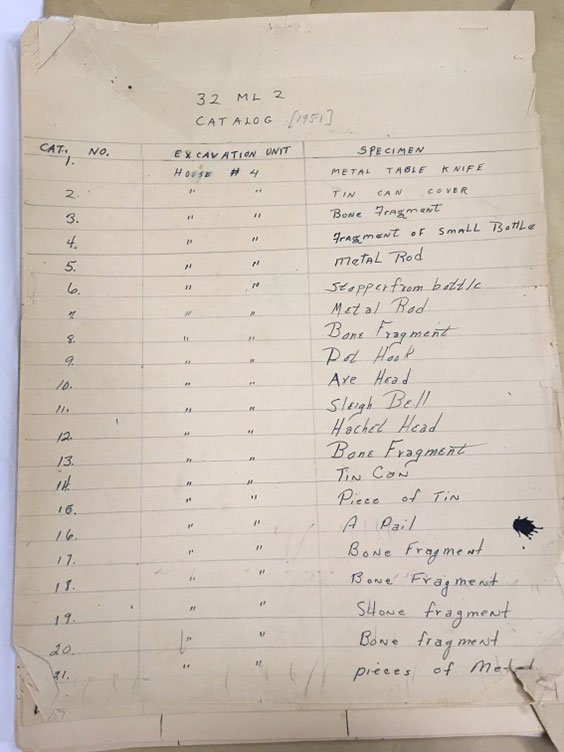
A field catalog for artifacts recovered during the 1951 excavation of Like-A-Fishhook Village in 1951 (AHP Archaeology files). Because we know which houses were occupied by Mandan and/or Hidatsa and which houses were occupied by Arikara families, knowing from which houses these objects originated is very important (House 4 was located in the Mandan-Hidatsa section of the village).
Imagine a projectile point that someone found in North Dakota. Perhaps they have mounted it in a frame in their home. From its shape and the technological style, I may be able to tell you that it is from the Archaic period. But that is about it. If it is an Oxbow point (for example), then it merely provides evidence that Oxbow technology is represented in North Dakota. It might be aesthetically beautiful, even ideal for exhibit. But it cannot tell us any more about human behavior and innovation in the past, which is actually what archaeologists are all trying to understand. Because at the end of the day, archaeologists are interested in understanding people, not things.
Now let’s imagine that the same point was scientifically excavated. We know from the additional excavation units around it that the point was found at a large camp site in Bismarck. Its vertical location (where it falls in soil stratigraphy) may tell us how old it is, or where it falls in time relative to other artifacts at the site. The artifacts found around it may help us understand what was going on in that spot. For example, if it was found in a pile of animal bone and cutting tools, we could infer that someone was likely butchering animals for food. If it was found in a pile of stone chipping debris and next to an antler pressure flaker, a different story emerges – perhaps this was a lithic workshop where stone tools were being manufactured. If a piece of charcoal found in its vicinity can be dated, then we can come up with a more exact age for the artifact. All of this information is documented during an excavation through extensive note-taking, sketching, photography, and mapping. And those records eventually make their way to the North Dakota Heritage Center & State Museum.

A field catalog from the excavation of the Flaming Arrow Village site (32ML4) in the early 1980s.

Entry made by crew member on July 20, 1971, while excavating the Hidatsa village of Amahami in Stanton, ND.
When I tell people that I am an archaeology collections manager, they typically assume that I only take care of artifacts. They are often surprised to learn that a huge and incredibly important part of doing archaeology includes creating, archiving, and referencing these paper records and photos. This also surprises archaeology students, who find themselves spending an inordinate amount of time sweating over notebooks or trying to draw wall profiles while wrestling graph paper in gusty winds during field school. This is actually a big responsibility from a preservation standpoint-- once the excavation is over, these paper records will comprise the most complete existing record of the site (or that portion of the site). In fact, when any archaeology contractor or state or federal agency submits collections for long-term curation, we require all the paperwork associated with their recovery from the field to be included.


A general level/feature level excavation form, which is filled out for every excavated level (this one was filled out for the level that was at a depth of 95-110 cm). The associated sketch is the plan map drawn to illustrate what the bottom of this particular level looks like. It documents important observations like soil color and texture, artifact content and density, etc. This feature form is from an excavation at Double Ditch Indian Village Historic Site (32BL8), Feature 709, Ditch 4.
We curate these in acid-free, archival folders and boxes and index them now so they are easier for scholars to query when researching our collections. I have never had a researcher request access to collections without also requesting access to the associated paperwork. When we do not have the paperwork providing context for a given collection, the researcher often has to exclude those objects from his/her study. That should give you a sense of their importance!


Photos of features in House 3 at Huff Village (32MO11), 1960.
So the next time you visit our State Museum or state historical site interpretive centers, remember that behind every artifact we are able to say anything about, there is likely a box of associated notes and photos that helped us tell that story.

