One day when he was a 15-year-old North Dakota farm boy, Lawrence Welk’s plow hit a rock, jerking him headlong onto the ground. When he got up, he realized his left arm was broken. He later told his biographer, Mary Coakley, that he wept, not from the pain, but because he feared he might never play the accordion again. Of course, we know that didn’t happen. Before his arm had even recovered, he figured out how to run a sling around his left knee, tie it to the accordion, pump with his knee, and play the instrument with just his right hand.
This year has felt a little like playing the accordion with one hand. Everyone has dealt with exceptional stress and uncertainty, and many, including several of my friends and acquaintances, have faced personal tragedy and loss. It’s been a tough year by any measure.
But at times like these, we need encouragement the most. Looking back on this year, I’m incredibly proud of our team at the state historic sites. Like Lawrence Welk strapping an accordion to one knee, staff worked with tenacity to make sure 2020 was anything but a lost year. Though many of the sites had fewer visitors, staff at these sites took advantage of the quieter season to achieve restoration and maintenance goals. Here are a few of the highlights from five sites I manage.
At the Former Governors' Mansion State Historic Site, Site Supervisor Johnathan Campbell achieved a long-term goal of restoring the front vestibule. Because the circa 1980 wallpaper was starting to peel, he did some investigation and found a small area of original textured plaster finish from the early 20th century that had survived intact behind a row of coat hooks. He then carefully recreated this brocade finish throughout the rest of the vestibule, including texturing, sanding, color-matching, painting, and applying a contrasting wash. Additionally, he repainted the radiator its original gold color and replaced the modern light switch with a historically accurate push-button switch made of brass and mother-of-pearl. This often-overlooked room is now a gem of skilled restoration.
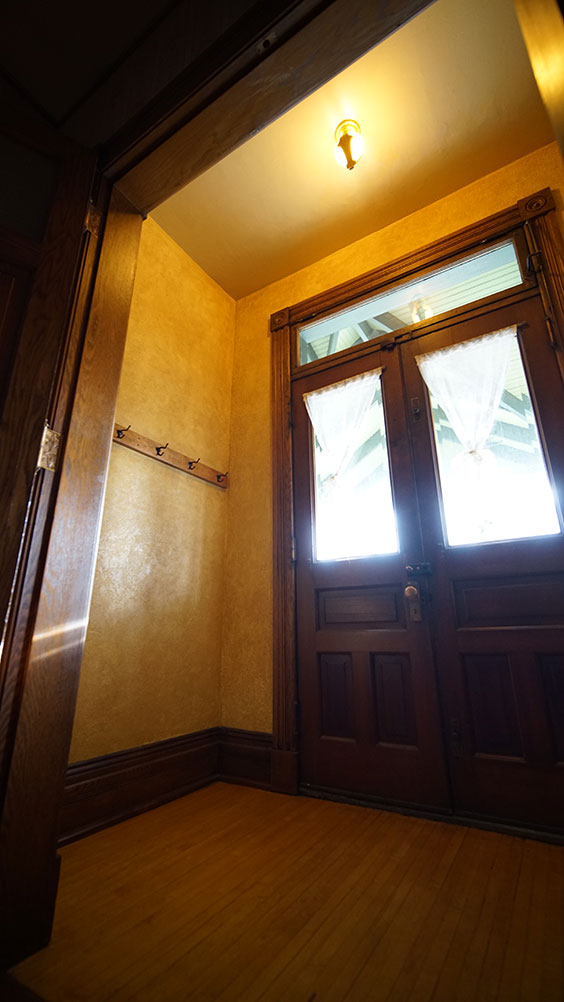

Site Supervisor Johnathan Campbell recreated this historic brocade finish in the Former Governors’ Mansion vestibule.
At Whitestone Hill State Historic Site, our new site supervisor, Stewart Lefevre, began removing lichen growth from the soldiers’ headstones. Marble, given the conditions on the North Dakota prairies, is not nearly as permanent as one might think. Overly powerful chemicals or abrasive tools can easily damage the surface. With advice from staff in Bismarck who have done similar cleaning projects, Stewart tested incrementally more powerful tools to ensure there were no adverse effects. He eventually found a combination that removed the lichens without harming the stone. He hopes to continue this work next summer.
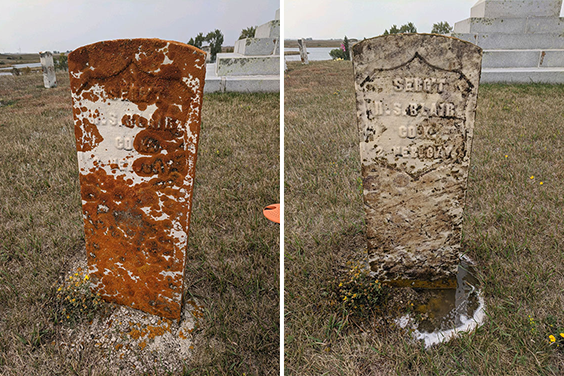
Stewart Lefevre, site supervisor at Whitestone Hill State Historic Site, was able to remove the lichens on this headstone, left. The remaining discoloration, right, will diminish naturally over the winter, but we will apply additional cleaners next season if necessary.
Meanwhile, we started a new mowing pattern at Whitestone. We let more of the prairie grasses grow, but mowed meandering paths through them. This more naturalistic approach still required Stewart to make sure that noxious weeds did not have a chance to take root and spread. We were soon stunned with the results as we watched hundreds of native wildflowers bloom across the site.
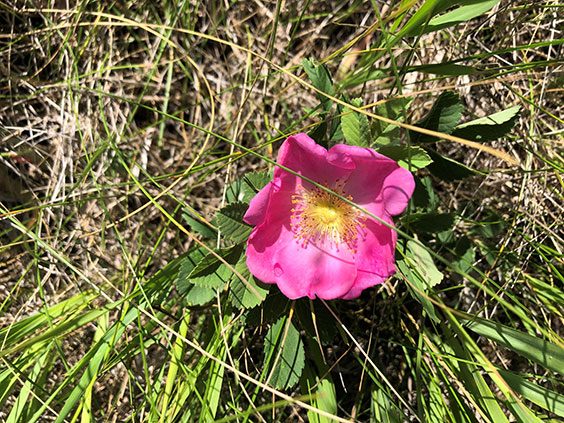

North Dakota’s state flower, the wild prairie rose, has thrived at Whitestone Hill State Historic Site following our new mowing regimen.
At Pembina State Museum, Site Supervisor Jeff Blanchard and his team removed dead, non-native landscaping from the front entrance area and began research on native replacements. Soon an ethnobotany garden will greet visitors. Each plant in the garden will illustrate the many purposes that Ojibwe, Métis, French-Canadian, and other people of the region found, including plant names in their various languages.
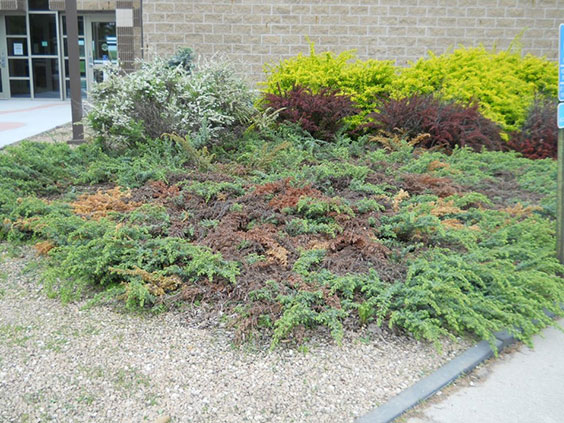

Pembina State Museum staff removed dead plants and hundreds of pounds of landscaping rock to make room for an ethnobotany garden, which will be planted in the spring.
At Stutsman County Courthouse State Historic Site, the site supervisor, Steve Reidburn, applied one of his great skills and hobbies—woodworking—to the new civics exhibit. He created display case bases that protect original courthouse objects while mimicking the look of historical office desks. The results speak for themselves.
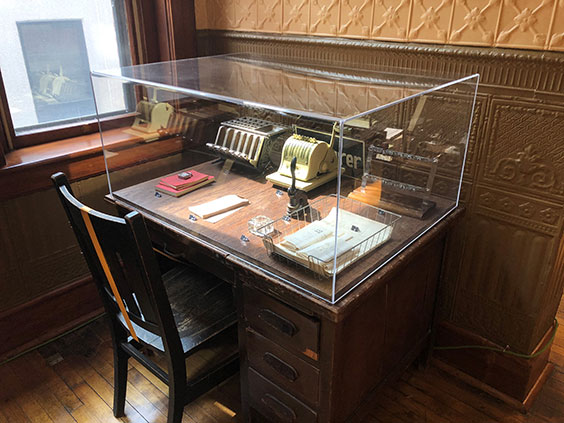

One of the display bases Site Supervisor Steve Reidburn made for the 1883 Stutsman County Courthouse State Historic Site.
At Welk Homestead State Historic Site, Site Supervisor Brian Grove, his staff, and local volunteers managed to repaint the blacksmith shop, granary, and garage, using a high-tech primer that should last for many years, if not decades. They also established a Gemüsegarten (vegetable garden), which included heirloom varietals of popular German-Russian crops, among many other improvements to the grounds.
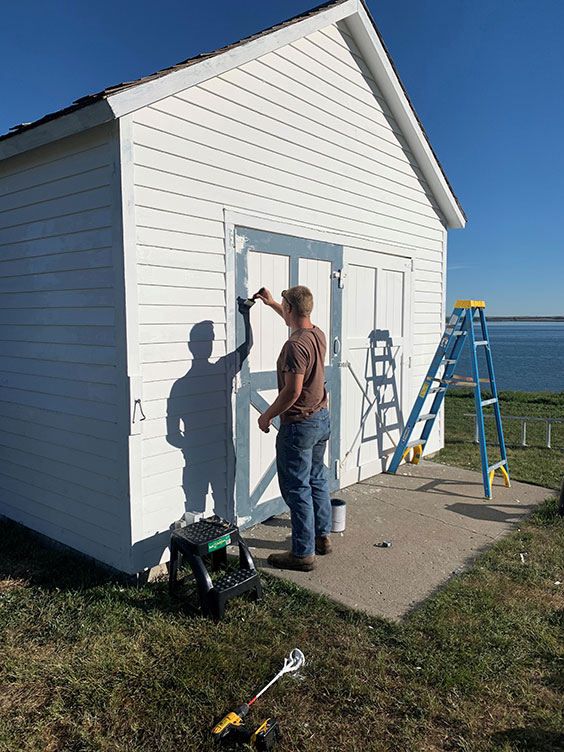

A volunteer helps us repaint the granary at Welk Homestead State Historic Site.
This short list of highlights doesn’t even touch on the many capital improvement projects that also took place at sites (most of which were done by professional contractors), or the numerous other projects at those sites managed by my colleagues Fern Swenson and Chris Dorfschmidt.
Although many staffed sites saw fewer visitors due to cancelled events and reduced travel, we were surprised to learn that total visitation at our sites actually went up 44% in 2020. The increase in socially distanced visits to our quieter unstaffed sites, especially Double Ditch Indian Village State Historic Site, more than made up for the decrease in foot traffic elsewhere.
We’re glad our historic places, which have seen hundreds of years of tragedy and joy and have even survived other pandemics, were able to help ground people during uncertain times. When you do visit again, we hope you’ll be encouraged by the hard work our staff has done.

