Saving Double Ditch: The Impossible Task of Stopping a Flooding River
It is a rare occasion during March that I am moved from the couch and into the great outdoors. On this particular day though, I was moved to visit Double Ditch State Historic Site, a historic site and recreational area about eight miles north of Bismarck. Once home to a thriving Mandan earthlodge village occupied from the late 1400s to the late 1700s, the site boasts 24 acres overlooking the Missouri River. Between the rolling mounds and deep depressions (the remnants of a village with a population exceeding 1,000) there is a trail that leads to the river. The grass is green, the sky is blue, and the air is crisp—it is a perfect day for a visit to Double Ditch.

An aerial view of Double Ditch State Historic Site. Note the two fortification ditches for which the site is named.
In my job, I manage many historic sites—more than 20 actually, but Double Ditch is special. On a day like this, I feel a true connection to these early Americans. Walking through the village, I am reminded again that 10 generations of Mandan Indians thrived here, and this was a major center for trade. I am also reminded that I have no idea where my great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great grandfather lived. Likely, I will never know. To preserve a place like this is a great honor and is not a responsibility I take lightly. The site is of great significance to people of Mandan ancestry--a group that lives today throughout much of North Dakota and the Northern Great Plains.
In marked silence I make my way to the edge of the river bank, my thoughts swirling with the sights and sounds that once would have greeted me. I pause when I approach what is now a familiar site: barbed wire and orange traffic cones dividing a crumbling, deteriorating path. The wire and traffic cones exist to warn approaching visitors to the perils ahead. And perilous it most certainly is... one step ahead and there is a 30 foot drop into a slump created by the erosion of the river bank. Thirty feet you say…? Let’s remember that a 30-foot drop is the equivalent of stepping off a three- story building. Imagine, if you will, walking up three flights of stairs and hurling yourself off the edge. If I were to continue down the existing walking path, I would most certainly fall over the edge, and the likelihood that I would crawl back out is slim. If I haven’t made my point clear—it is a long and dangerous drop. Alarmingly, this drop and the ensuing gap between the village proper and detaching bank continue to widen as the area has become structurally unsound and continues to shift at an accelerated rate.
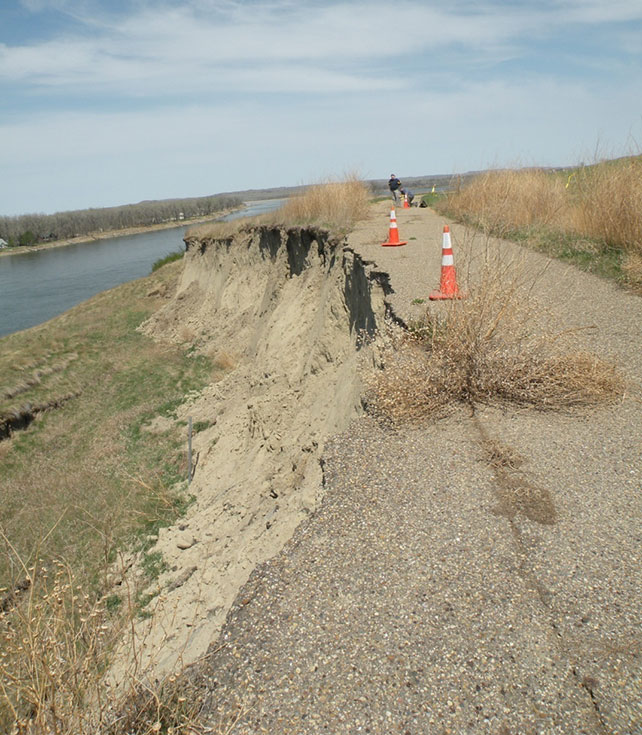

The erosion of the bank and destruction of the walking path at Double Ditch, April 2015.
The extensive erosion of the bank began in 2011 due to the massive flooding of the Missouri River. At that time, President Barrack Obama declared much of North Dakota a disaster area, and more than 12,000 people were evacuated from their homes. Many communities were at risk of destruction due to the massive flooding, and Double Ditch was no exception. It would take several seasons before the true extent of the damage to the site would be known, as erosion tends to be a silent and shadowy nemesis.
As you are reading this, the bank continues to slump. Most troubling, however, is the increasing number of human burials that are exposed due to the erosion. As of publishing time, there have been 14 Native American burials exposed since April of 2013.

Artist Robert Evans’ depiction of Double Ditch Indian Village, circa 1550. This cylorama mural can be seen in the State Museum of the North Dakota Heritage Center in Bismarck in the Innovation Gallery: Early Peoples.
Archaeology is often associated with an “Indiana Jones” type character. We have all seen the image of a handsome leading man unearthing a human skeleton, small brush in hand, sweltering in the hot desert sun. This, however, is an invention of Hollywood and couldn’t be further from the truth. The archaeologists of today are highly trained men and women who study the activity of humans in the past. They do this by scientifically collecting cultural material—and on most occasions, actively AVOIDING human burials out of cultural sensitivity and respect for tribes.
We have an amazing and talented team of archaeologists working for the State Historical Society. Their specialties include pottery, lithics, cartography and ethnohistory.; These are not cave-exploring, torch-baring, rope-swinging individuals. These are real people that now routinely unearth and relocate human remains due to the erosion at Double Ditch. Each burial removal is conducted by our staff with great care, respect and dignity. It’s challenging work that can take an emotional toll on those working with so many human remains. As the rate of erosion is accelerating, so are the numbers of human burials exposed.

Aerial photo of the slumping (rotational erosion) of the bank at Double Ditch State Historic Site. The lighter colored area below the site is newly exposed—a direct result of the erosion of the bank.
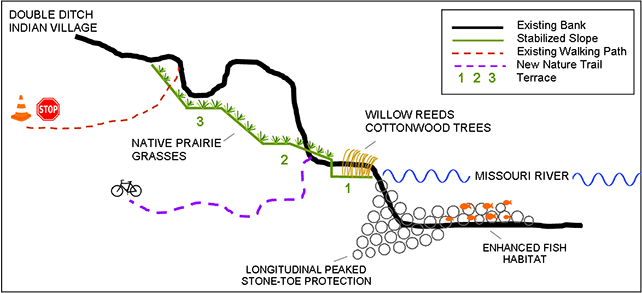
There is, however, a solution to this problem. A concept has been proposed by an engineering firm to stabilize the bank at Double Ditch. As the slumping is so extensive (2,000+ linear feet of bank need to be stabilized) it will not be quick or cheap. We cannot, for lack of a better phrase, “slap a band-aid on it.” The bank will be stabilized by inserting a longitudinal peaked stone toe into the bank. The work will also include the creation of several terraces, a new walking path and as a result, a better fish habitat in the river. The price tag for all this is an estimated 3.5 million dollars.
In the 2015 legislative session, the State Historical Society requested one-time funding to stabilize the bank at Double Ditch. For those of you unaware, state agencies (such as the Historical Society) must have their budgets approved by the governor, and then by both the Senate and House of Representatives every two years during the legislative session. One-time requests such the funding for Double Ditch are heavily scrutinized by both sides before a decision is made. Leaders of the State Historical Society, interested parties, and community representatives often testify before both the House and the Senate to support funding requests. It is an arduous process.
Our budget, or Senate Bill 2018, with the 3.5 million dollar request, was a contentious point between the Senate Appropriations Committee and the House Appropriations (Education and Environment Committee). Considerable press coverage by the Bismarck Tribune and Fargo Forum added pressure to a political hot button issue. In the end though, strong support from the Governor's office, the Mandan, Hidatsa and Arikara Nation, the Indian Affairs commissioner and the North Dakota Senate prevailed. The bill was passed on April 28, 2015, with funding included to stabilize the bank at Double Ditch.
We are relieved that work can begin on this very necessary and long-awaited project. We are looking forward to preserving this magnificent Mandan village that was occupied for nearly 300 years, a true gem on state land.
Stay tuned for more information and a follow-up post on the progress we've made out at Double Ditch!
Author’s note: Please take caution when visiting Double Ditch State Historic Site. If you wish to see the erosion of the bank, please do so at a safe distance. Also, it should be noted that to remove any items from a state owned archaeological site is a felony and prosecutable by law.





