Behind-the-Scenes: School Tours of the North Dakota Heritage Center
“My favorite quote from a student this year as she was exiting one of the exhibits was, ‘I love this place.’ Her eyes were wide open and she had a look of pure joy on her face. I bring my students there to be able to have these great experiences.” (Jessica Horst Frohlich, 4th grade teacher at Northridge Elementary)
If you’ve ever visited the North Dakota Heritage Center & State Museum on a weekday in April or May, chances are good that you have seen a swarm of elementary school students and their teachers enjoying themselves. As late spring weather warms up, and the average 5th grader’s thoughts begin to stray from the classroom, we begin to see huge numbers of students and teachers touring the exhibits, learning about the history of North Dakota, and generally having a great time!

Fifth grade students from Will-Moore Elementary School in Bismarck are welcomed to the North Dakota Heritage Center & State Museum by Becky Barnes of the North Dakota Geological Survey and Timothy Reed of the State Historical Society of North Dakota prior to receiving a behind-the-scenes tour of laboratory and collections areas.
Many staff members here love the heightened activity this time of year brings. We enjoy seeing large numbers of young people in the galleries. These students represent the future of North Dakota; full of potential and curiosity, mindful of our shared history, and eager for opportunities to discover and grow. Translation: you’re likely to find a bunch of kids here ready to learn and have some fun!
We host dozens of school group tours during the last month or so of the academic year. Sometimes we’re able to offer a behind-the-scenes tour of our non-public areas to these visiting school groups. Staff availability doesn’t always allow us to invite every group into our non-public spaces, but when it works out, students can gain a unique appreciation of what it can be like to work in a museum as they visit with staff.

Fifth grade students from Will-Moore Elementary School in Bismarck are given a short introduction to the archeology lab and artifact collections storage areas by Archeology & Historic Preservation Division staff Timothy Reed and Meagan Schoenfelder.
We were recently able to offer this experience to a large number of 4th graders from Northridge Elementary School in Bismarck, and also to a group of 5th graders from Will-Moore Elementary of Bismarck. During their visits, these groups visited the archeology laboratory and collections areas that are normally inaccessible to visitors. They were also fortunate to get a tour of the North Dakota Geological Survey’s paleontology laboratory and collections areas.
I’d like to thank Ms. Horst Frohlich of Northridge Elementary, along with Ms. Wetch and Mr. Schultz of Will-Moore Elementary for bringing their students here, and for helping them engage with North Dakota’s past outside the classroom. I’m glad we could accommodate your requests for a behind-the-scenes tour for your students!
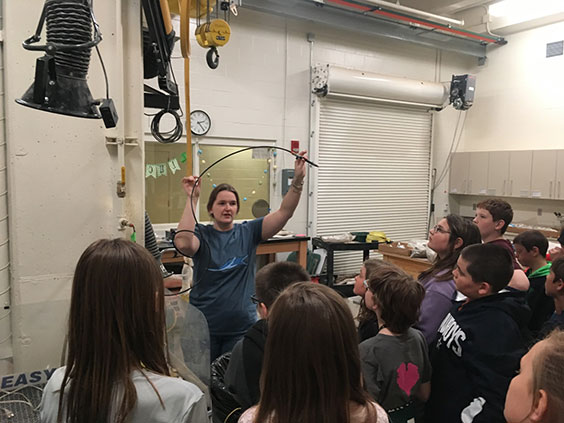

Becky Barnes of the North Dakota Geological Survey describes a laboratory procedures used to prepare fossils to the 5th grade students from Will-Moore Elementary School of Bismarck in the Johnsrud Paleontology Laboratory at the North Dakota Heritage Center & State Museum.
From July 2016 through June 2017, we welcomed 220,000+ visitors of all ages through our doors. Looking specifically at school groups, we saw 9,294 students representing 56 communities during that same period. More recent numbers reveal that 4,000+ students visited in May 2018 alone!
With so many visitors concentrating their visits during the end of the school year in April and May, it’s important to also extend an invitation to students and educators to visit during the rest of the school year. Take advantage of all the Heritage Center & State Museum has to offer all year round! If you’re an educator, please consider scheduling an additional trip to the North Dakota Heritage Center during the fall or winter months. Kids are no less curious when it’s cold, and many discoveries await them in our galleries and labs!

A 5th grade student from Will-Moore Elementary School of Bismarck proudly points to a relative’s image displayed in the Innovation Gallery: Early Peoples at the State Museum.